Coat color - dogs
Introduction to coat colour in dogs
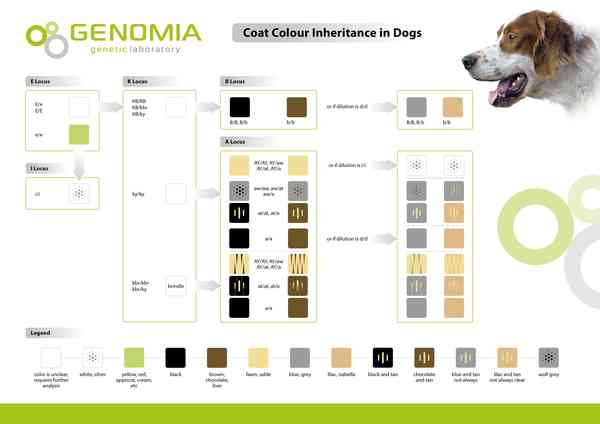
Coat colour is influenced by the production of the two main pigments eumelanin (brown to black pigment) and pheomelanin (light to brownish red pigment). In most mammals, the synthesis of eumelanin or pheomelanin is regulated by two key genes, MC1R (locus E) and ASIP (locus A). In domesticated dogs, a third gene, CBD103 (locus K), also plays an important role. Several other genes have been identified in relation to coat colour in dogs, e.g., TYRP1 (locus B), MLPH (dilution locus D), MFSD12 (dilution locus I), etc.
In the inheritance of colour, the hierarchy and interactions of the most important genes involved in coat colour are described. The MC1R gene has an epistatic (superior) effect to the other genes responsible for coat colour, i.e., it can block the expression of alleles at another locus so that the expected trait is not expressed at all:
-
In the presence of the e/e genotype, pheomelanin is produced and the resulting colour of the individual is due to this pigment regardless of the genotype of the other loci.
-
In the case of the E/e or E/E genotype, the K locus and the A locus play a significant role in the resulting colour.
-
dark coat colour can be expected if at least one KB allele (black allele) is present, i.e. if/where genotypes KB/KB, KB/ky, KB/kbr are present
-
in the presence of ky allele (yellow allele), i.e., genotypes ky/ ky, ky/ kbr or the kbr allele (brindle allele) responsible for light and dark brindling, i.e., genotype kbr/ kbr, locus A determines the resulting coat colour:
-
In the presence of a allele (genotype a/a), eumelanin (brown to black pigment) is expressed,
-
in the presence of A allele (genotypes ay/ay, ay/aw, ay/at, ay/a, aw/aw aw/at, aw/a, at/at, at/a), the resulting colour is affected by the production of pheomelanin (light to brownish red pigment) or the coat is brindled if at least one kbr allele (brindle) is present.
-
-
.
The system of the hierarchy of alleles described above determining the coat colour of dogs is shown in the following diagram:
.
List of loci and their alleles (known as of 09/2021) tested in the Genomia laboratory
The dominant allele is highlighted in bold. If the allele is dominant, it is sufficient for its expression in the offspring to inherit it from only one parent. In the case of a recessive allele, the individual needs to inherit these alleles from both parents so that the trait gets expressed.
.
Locus
A (to order the test and for more information continue here:
https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/locus-a-dog/)
A (ay >aw> at), and
-
ay: fawn
-
aw: agouti (wolf grey)
-
at: tan (black body with red on muzzle, eyebrows, chest, and legs)
-
a: recessive black
Locus B (to order the test and for more information, continue here: https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/locus-b-dog/)
-
B: black
-
b (bs, bc, bd, baus): brown
Locus Cocoa for French Bulldog (to order a test and for more information continue here: https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/cocoa/)
-
Co: normal pigment
-
co: cocoa
Locus D - eumelanin dilution (to order the test and for more information continue here: https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/locus-d-dog/)
-
D: normal pigment without dilution
-
d (d1, d2, d3): diluted pigment, turns black to blue and brown to isabella
Locus E (to order the test and for more information continue here: https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/locus-e-dog/)
-
E: dark to black
-
e: red to yellow
-
EM : melanistic mask, production of the dark pigment eumelanin localized to the face (to order the test and for more information continue here: https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/locus-em/)
-
EH : sable colour in English and American Cocker Spaniels (to order a test and for more information continue here: https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/locus-eh/): https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/locus-eh/)
-
EG : Grizzle colour in Saluki and Domino colour in Afghan Hounds (to order the test and for more information continue here: https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/locus-eg/)
Locus I - dilution gene (to order the test and for more information continue here: https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/locus-i/)
-
I: normal pigment without dilution
-
i: dilutes pheomelanin to a light to white colour
Locus
K (to order the test and for more information continue here:
https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/locus-k/)
KB > kbr > ky
-
KB: dominant black
-
kbr: brindle (brindled, alternating eumelanin and pheomelanin)
-
ky: yellow - recessive yellow
Locus M (to order the test and for more information continue here: https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/merle/)
-
m: without merle
-
Mc: cryptic merle
-
Md: dilution merle
-
M: merle
-
Mh: harlequin
Locus S - spotting, to order the test and for more information continue here: https://www.genomia.cz/cz/test/spotting/)
-
S: without white marks
-
sp: Piebald, extensive white spots
-
sw: completely white coat
-
si: Irish spotting, small white spots often forming a white collar or belly